Medical Hair Loss Therapy
Dermatologist-led Clinical Therapies to Treat Hair Loss and Scalp Disease.
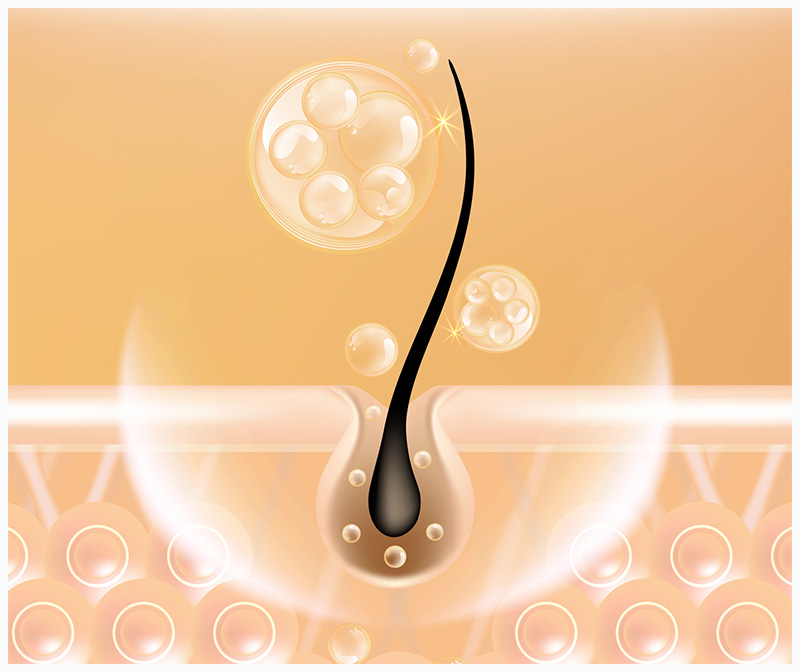

Male Hair Loss Therapy Options
1 CAPSULE. 2 EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
For most people, we recommend the 2 in 1 hair capsule. This is because studies show capsules and pills are slightly more effective than topical medicines. Patients are also more likely to continue to take a capsule long term, which ensures the highest likelihood of success for your hair growth.
DHT blocker prevents miniaturization
Minoxidil 2.5mg
Improves blood flow and helps hair grow thicker

All-In-One Scalp Solution
1 SOLUTION. 3 EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
An effective alternative to oral medications, the 3-in-1 scalp solution is designed to maximize absorption and hair growth. Studies show we reach 95% of the benefits of the oral medication with only half as much systemic absorption. While both forms are safe and well tolerated, if you are worried about taking a capsule, this is the plan for you.
Female Hair Loss Therapy Options
All-In-One Hair Pill
1 CAPSULE. 2 EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
For most women, we recommend the all-in-one hair capsule. This is because studies show capsules and pills are slightly more effective than topical medicines. Patients are also more likely to continue to take a capsule long term, which ensures the highest likelihood of success for your hair growth.
Spironolactone 100mg
Blocks male sex hormones for women over 45
Dutasteride 0.5mg
Blocks male sex hormones for women over 45
Minoxidil 1.25mg
Improves blood flow and helps hair grow thicker

All-In-One Scalp Solution
1 SOLUTION. 2 EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
An effective alternative to taking oral medications, the all-in-one scalp solution is designed to maximize absorption and hair growth. Studies show we achieve 95% of the benefits of the oral medication with only half the systemic absorption. While both forms are safe and well-tolerated, if you are worried about taking a capsule, this is the plan for you.
Minoxidil 7%
Improves blood flow and helps hair grow thicker
Retinoic Acid 0.001%
Improves absorption
Injectables
Exosomes and Hair Loss
A new treatment for hair loss is getting a lot of attention lately. It’s called exosomes, and many people claim it is very effective. So what are exosomes, and how can they help with hair loss? In this article, we will discuss exosomes and how they can be used to treat hair loss. We will also discuss the research on this topic and answer some common questions about exosomes and hair loss.
There is a growing body of evidence that exosomes can be used to treat hair loss.
One study found that exosomes derived from stem cells can promote hair growth in mice. The exosomes in this study were taken from human embryonic stem cells. When these exosomes were injected into mice, they stimulated the growth of new hair follicles. The exosomes also increased the number of follicles that entered the anagen (growth) phase.
Another study found that exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells can also promote hair growth. In this study, exosomes were taken from human adipose-derived stem cells and injected into mice. The exosomes stimulated the growth of new hair follicles and increased the number of follicles that entered the anagen (growth) phase.
A third study found that exosomes derived from dermal papilla cells can also promote hair growth. In this study, exosomes were taken from human dermal papilla cells and injected into mice. The exosomes stimulated the growth of new hair follicles and increased the number of follicles that entered the anagen (growth) phase.
These studies suggest that exosomes can be used to treat hair loss. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
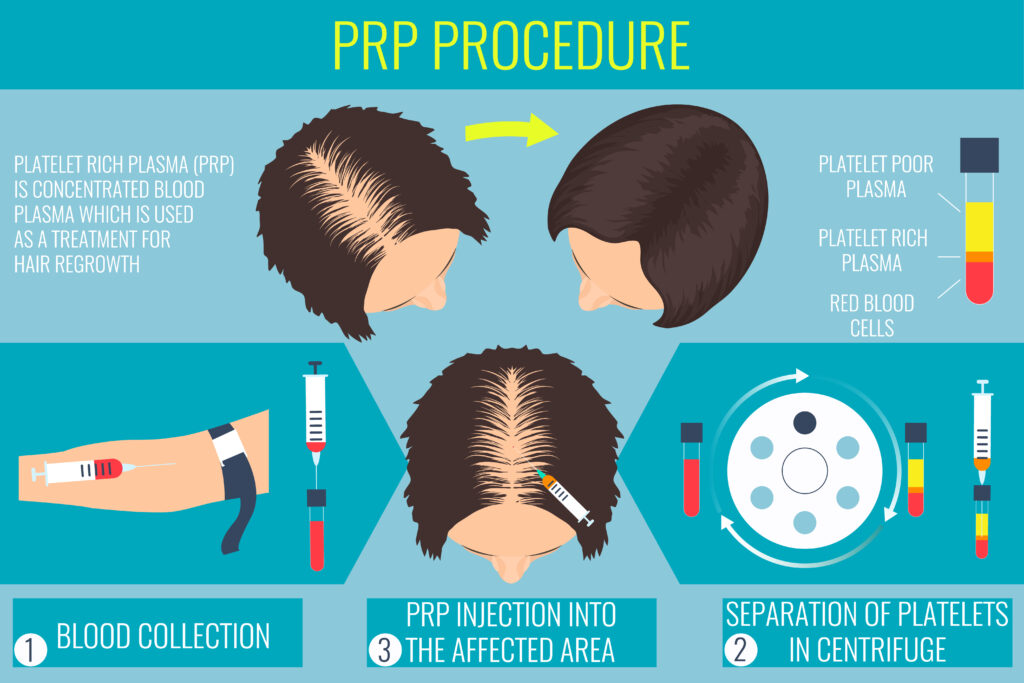
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a therapy that involves the injection of a concentrated solution of platelets and plasma into the skin or scalp. The concentration of platelets is typically 2-8X the whole blood native concentration.
Platelets are a type of blood cell that play a crucial role in the healing process.
They contain growth factors and other signaling molecules that stimulate the repair of damaged tissue and promote new cell growth. Plasma is the clear, straw-colored fluid portion of the blood that contains proteins, electrolytes, and other substances. PRP has been used since the mid-90s and is FDA-cleared as a class II medical device.
Combination therapy
PRP may be used as a standalone therapy or in combination with other treatments, such as microneedling or topical medications. However, there is some controversy over the effectiveness of PRP, as the results of studies have been mixed and more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of PRP is not fully understood, but it is thought to work by providing a burst of growth factors and other signaling molecules to the area being treated. These growth factors stimulate the production of new collagen, elastin, and other components of the extracellular matrix, which in turn helps to repair damaged tissue and promote the formation of new blood vessels. Some growth factors thought to be involved are as follows:
EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor) – promotion of epithelial cell growth, angiogenesis, promotion of wound healing
FGF (Fibroblast Growth Factor) – tissue repair, cell growth, collagen production
PDGF (Platelet Derived Growth Factor) – cell growth, new generation and repair of blood vessels, collagen production
VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) – growth and new generation of vascular endothelial cells
TGF-B (Transforming Growth Factor Beta1) – growth of epithelial cells, endothelial cells , promotion of wound healing
KGR (Keratinocyte Growth Factor) – growth and new generation of keratinocyte
PRP may also be used in combination with hair transplantation to improve the success of the procedure. Some studies have shown that PRP can improve the survival rate of transplanted hair follicles, leading to better results and more natural-looking hair.
Key benefits of PRP in hair transplantation:
“Jump starts” healing process
Provides provisional matrix or scaffold for healing
Improves hemostasis
Post surgical implications
Anti-inflammatory properties
Anti-microbial properties
